Understand Your Air Conditioning System
 Whether you’re in the market to install a new air conditioner , looking for an air conditioning contractor near you or you are looking to get your system repaired, it helps to do your homework, so you can discuss your home cooling needs and compare multiple bids from A/C contractors. Learn the terminology of air conditioning with this easy-to-understand glossary.
Whether you’re in the market to install a new air conditioner , looking for an air conditioning contractor near you or you are looking to get your system repaired, it helps to do your homework, so you can discuss your home cooling needs and compare multiple bids from A/C contractors. Learn the terminology of air conditioning with this easy-to-understand glossary.
A/C -- A/C is short for “air conditioning.”
A/C condenser -- The condenser is the outdoor fan unit of your A/C system. By removing the heat from the refrigerant gas, it condenses it back into liquid form.
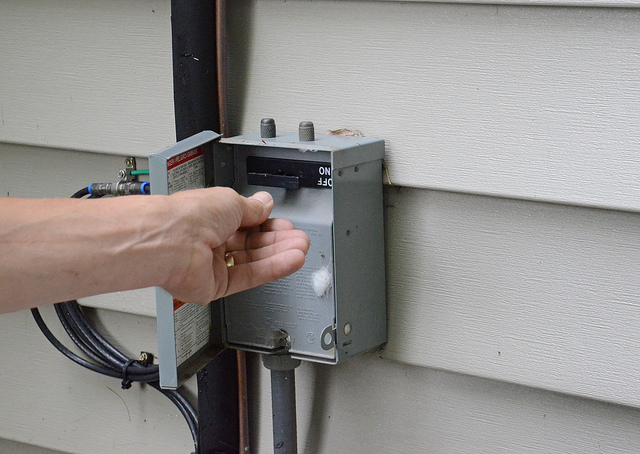
A/C disconnect – Your air conditioning disconnect is the main power switch, located near the condenser.
Central air conditioning -- Central air conditioning is a system that’s designed to condition the air of your entire home. A centralized unit, usually positioned outdoors, cools and dehumidifies the air before circulating it via your ductwork.
Compressor -- The main component of your cooling system, the compressor is a pressurizing device that transforms refrigerant from a gas into a liquid. This process, with the help of the A/C condenser fan, removes heat from the air.
Cooling load -- The cooling load refers to the amount of cooling which is necessary to maintain a specific indoor temperature (usually 78 degrees F) in summer, no matter what the outdoor temperature may be.
Dehumidifier -- A dehumidifier is an electrical device that extracts excess moisture from the indoor air, decreasing the relative humidity and making your home more comfortable. The maximum recommended level of relative humidity is 50 percent in summer.
Ductless air conditioning – See mini-split.
Ductwork -- Most homes are equipped with ductwork, a system of pipes, known as “ducts,” designed to transport cooled (or heated) air from your HVAC system and distribute it to the rooms of your home.
Energy Star -- The government’s Energy Star program certifies certain appliances, such as air conditioners, that meet their standards of energy efficiency.
HVAC -- The term HVAC stands for Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning.
Mini-split air conditioning -- Also known as “ductless,” mini-split air conditioning is an energy-efficient form of A/C, which does not require ductwork. It consists of an outdoor compressor and indoor air handlers (evaporators).
Refrigerant -- A refrigerant is a substance which is used to transfer heat, allowing your A/C to cool your rooms. It remains a gas at low temperatures and pressure. For years, Freon R-22 was the most common air conditioning refrigerant; however, systems using R-22 are being phased out and replaced by more environmentally friendly R-410A versions. The use of R-22 will be prohibited as of 2020.
Register -- A register is a grill installed over a heating/cooling duct. It can usually be adjusted to direct the flow of cool or warm air within the room.
SEER – SEER stands for Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio. To measure an A/C system’s efficiency, its total cooling output over the entire hot season is divided by the amount of energy it consumed during that same period. The SEER can range from 10 to 16; the higher the number, the more energy-efficient (and economical) the system is.
Thermostat -- A thermostat is a device used to regulate room temperature. An energy-saving programmable thermostat allows you to set temperature in advance, according to when the room will be occupied.
Window A/C – A window air conditioner is suitable for cooling one single room. It is convenient for renters, as it can be moved easily. However, it tends to be the least efficient home cooling method.
Zoned A/C – Zoned air conditioning is set up so that it can be operated independently in 2 or more different zones of your home. This conserves energy and lowers electricity bills.
Some of the above was adapted from http://www.homebuildingmanual.com/index.html.
Laura Firszt writes for networx.com.
Updated October 21, 2018.
Looking for a Pro? Call us (866) 441-6648

Heating & cooling Average Costs
HVAC Contractors Experiences

Air Conditioner Replacement In Florida’s 85-Degree Winter Weather

New HVAC Installation After My Furnace Failed Inspection



